The term "Industry 4.0" might appear as just another buzzword in the endless lexicon of tech jargon. However, it symbolizes a profound shift in how industries operate and serve their customers. But what exactly is Industry 4.0?
The Fourth Industrial Revolution
We are living in the era of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, a time where digital technology is seamlessly integrating into human lives and industries. Born from the fusion of technologies blurring the lines between physical, digital, and biological spheres, Industry 4.0 is revolutionizing traditional manufacturing and industrial practices.
The concept of Industry 4.0 hinges upon four key principles, which collectively aim to enhance the digital connectivity and efficiency of businesses. These principles include interconnection, information transparency, technical assistance, and decentralized decisions.
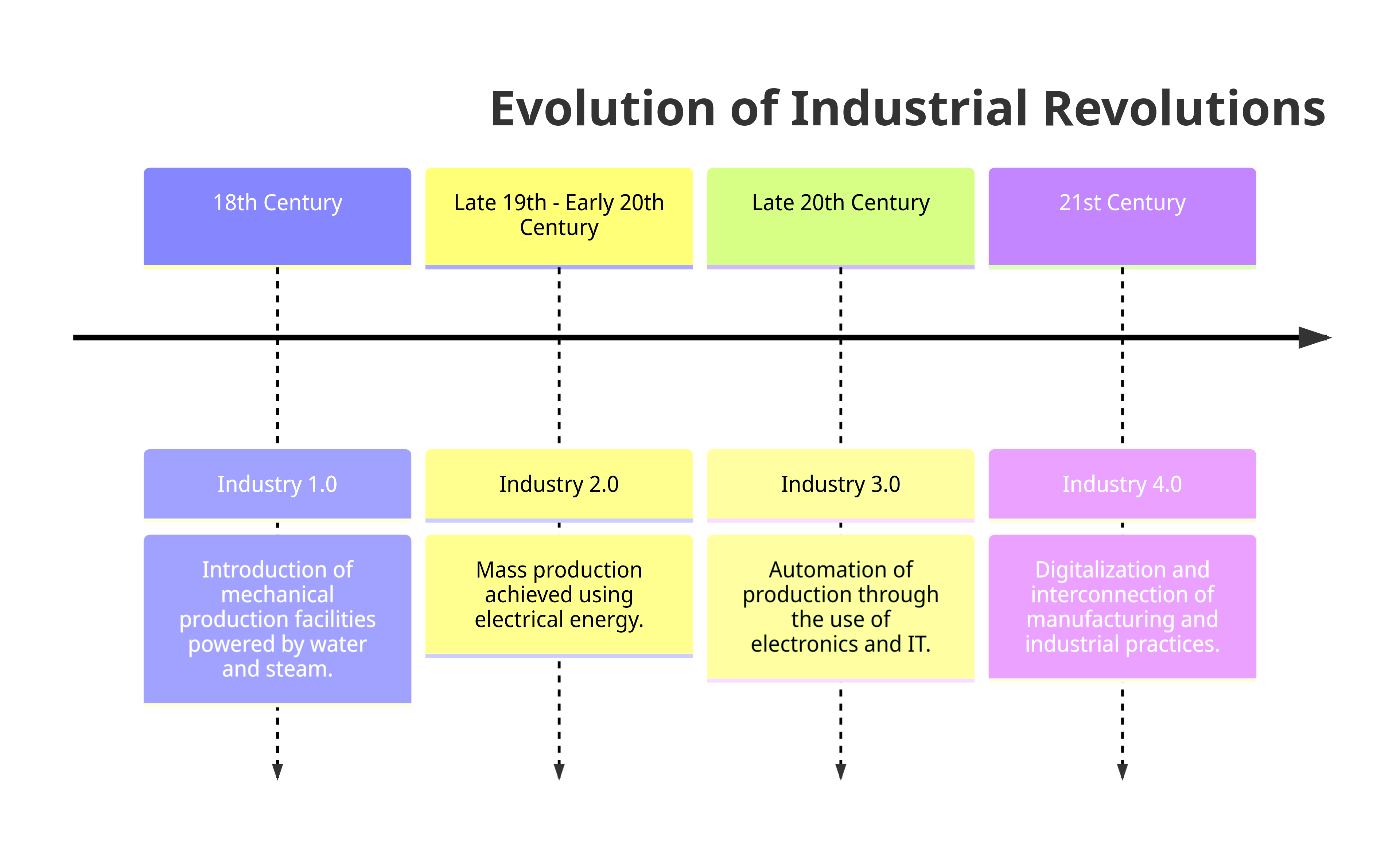
To understand the impact of Industry 4.0, we must first explore its predecessors:
- Industry 1.0: Introduction of mechanical production facilities powered by water and steam.
- Industry 2.0: Mass production achieved using electrical energy.
- Industry 3.0: Automation of production through the use of electronics and IT.
Each industrial revolution has dramatically transformed industries, paving the way for more advanced and efficient processes. However, none of them compare to the breadth and depth of changes that Industry 4.0 brings to the table.
An Era of Smart Factories
With the advent of Industry 4.0, the idea of a 'smart factory' has taken center stage. These factories, loaded with interconnected systems and predictive maintenance tools, can anticipate faults, adapt to changes, and optimize operations in real-time.
The smart factory concept embodies the idea of a flexible, adaptive manufacturing process that can be changed in response to evolving market conditions.
In these digitally-enabled settings, physical systems become Internet of Things (IoT) objects, able to collect vast amounts of data and communicate and cooperate with each other and humans in real-time. This fusion of the digital and physical worlds, underpinned by cyber-physical systems (CPS), lies at the heart of Industry 4.0.
Embracing Digital Transformation
Industry 4.0 is synonymous with digital transformation. But, it's more than just converting physical data to digital; it's about harnessing these digitized data to improve processes, products, and decision-making. As businesses grapple with ever-growing datasets, they are increasingly turning to Artificial Intelligence (AI) to glean valuable insights and optimize their operations.
AI is proving to be a game-changer, particularly in fields like predictive maintenance and customer service, where its ability to analyze trends and patterns can result in significant cost savings and improved customer satisfaction.
"AI's ability to analyze and learn from data makes it a vital tool in our journey towards Industry 4.0."
Technologies Shaping Industry 4.0
As we traverse deeper into the world of Industry 4.0, it's essential to delve into the key technologies driving this new era of industrial revolution. From Internet of Things (IoT) to artificial intelligence (AI), these technologies are reshaping industrial landscapes and paving the way for a more efficient and interconnected world.
Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT is the linchpin of Industry 4.0. It involves the interconnection of devices, enabling them to collect, share, and use data to improve processes. Industrial IoT (IIoT) systems monitor, collect, exchange, analyze, and deliver valuable new insights, driving smarter and faster business decisions.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial intelligence is rapidly transforming industries. Through machine learning, AI can analyze vast amounts of data, identifying patterns and trends that humans might overlook. This results in enhanced efficiency, predictive capabilities, and improved decision-making.
Augmented Reality
Augmented reality (AR) is another important technology in Industry 4.0. It overlays digital information onto the physical world, improving our understanding and interaction with processes. For instance, AR can assist in complex assembly tasks or maintenance operations, guiding technicians step-by-step through procedures.
Big Data and Analytics
The fuel driving Industry 4.0 is data. The ability to collect and analyze large amounts of data in real time is a significant benefit of the Fourth Industrial Revolution. Big Data and analytics are crucial in providing insights that can help industries predict trends, improve processes, and make informed decisions.
Cybersecurity
As industries become increasingly connected, the risk of cyber threats grows. The rise in cyber-physical systems and IoT devices has broadened the attack surface for potential cybercriminals. Cybersecurity measures are integral to protect sensitive data and maintain operations in Industry 4.0.
"As we venture deeper into Industry 4.0, cybersecurity is no longer an option, but a necessity."

The Impacts of Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 has far-reaching implications that go beyond manufacturing. It is reshaping business models, causing a shift from product-centric to service-centric models. This transformation, often referred to as Servitization, offers new revenue growth opportunities and competitive differentiation.
Industry 4.0 in Action and Its Future Prospects
As we understand the fundamental technologies and implications of Industry 4.0, let's explore how these ideas are implemented in real-life scenarios, challenges encountered, and the opportunities that await.
Industry 4.0 in Practice
The concept of Industry 4.0 is not just theoretical. Many companies are already embracing digital transformation. For example, predictive maintenance allows businesses to anticipate machine failures and act before they occur, significantly reducing downtime and costs. Another practical example is the use of AI in customer service, where AI technologies are employed to automate responses, reducing time and improving customer satisfaction.
Challenges in Industry 4.0
While Industry 4.0 is filled with opportunities, it also presents unique challenges. These include issues related to data privacy and security, the need for significant investment in digital infrastructure, and the training of employees to handle the new technology.
Future Prospects of Industry 4.0
The future of Industry 4.0 is full of potential. As more businesses embrace digital transformation, we can anticipate an increase in efficiency, productivity, and customer satisfaction. One exciting prospect is the development of digital twins, virtual replicas of physical systems that can be used to run simulations and optimize systems.
The path to Industry 4.0 might be paved with challenges, but the potential rewards make it a journey worth taking.
Conclusion
As we venture further into the Fourth Industrial Revolution, it's important to remember that Industry 4.0 is not an end, but a means to an end. Its ultimate goal is to improve our lives, whether by creating more efficient processes, reducing waste, or providing better services. By understanding and embracing Industry 4.0, businesses can position themselves for success in this new digital era.
Find out more about how Industry 4.0 is changing the landscape of customer service and after-sales support here.