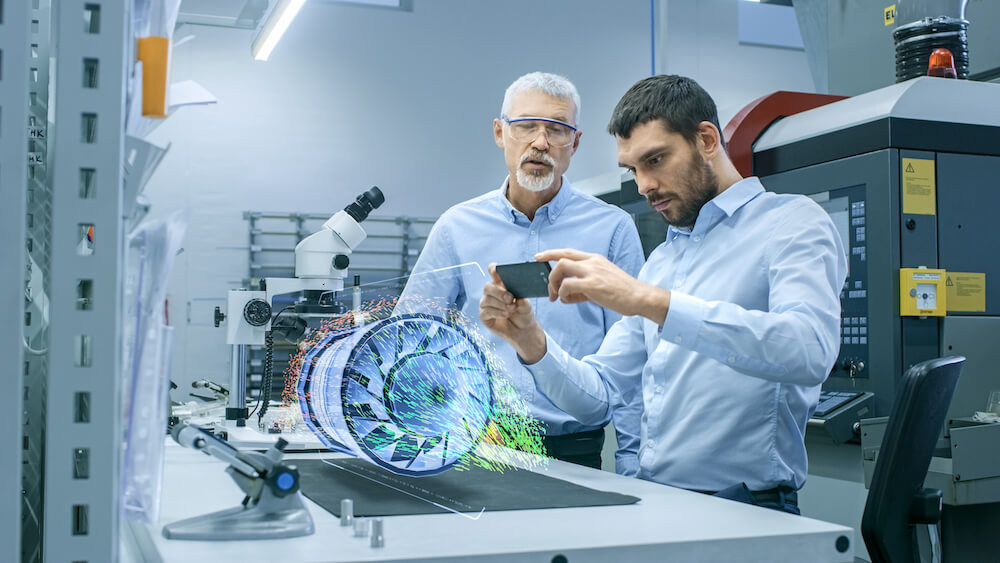

What is Augmented Reality?
Augmented reality (AR) refers to reality technologies that overlays digital content onto the real world, enhancing our perception and interaction with the real environment. Unlike virtual reality (VR), which immerses users in a completely virtual environment with special virtual reality headsets, AR integrates digital elements into the real world, making it a more seamless and interactive experience.
AR can be experienced through various devices, including smartphones, tablets, smart glasses, and headsets. Through the use of sensors, cameras and other hardware, AR-enabled devices can detect the user's location, orientation and movements, allowing virtual objects for example 3D objects to be placed and interacted with in the real world.
How Does Augmented Reality Work?
The main components that enable Augmented and Mixed Reality to work are hardware, software, and tracking. The hardware includes mobile devices such as cameras, sensors, and head-mounted displays that capture and process real-world information. The software comprises applications and algorithms that interpret the data collected by the hardware and overlay virtual content onto the real world. Tracking is the process of continuously monitoring the user's position and movements to ensure that the virtual content stays aligned with the real world.
Depending on how the virtual content is superimposed on the real world, AR can be divided into three main types:
- Marker-based AR: In this type of AR, a predefined marker or trigger image is used to activate the virtual content. When the camera of an AR-enabled device identifies the marker, it overlays the virtual content onto the marker, creating an augmented view.
- Markerless AR: Also known as location-based AR, this type of AR uses the user's location and natural environment as triggers to overlay virtual content. GPS, compass, and other sensors are used to determine the user's location and orientation, allowing virtual content to be placed in the real world accordingly.
- Projection-based AR: This type of AR projects virtual content directly onto real-world objects or surfaces, without the need for markers or location triggers. Specialized projectors are used to create the augmented view, and the virtual content aligns with the physical objects in real-time.
Applications of Augmented Reality
The potential applications of AR are vast and diverse, spanning across various industries. Here are some examples of how a augmented reality app is transforming different sectors:
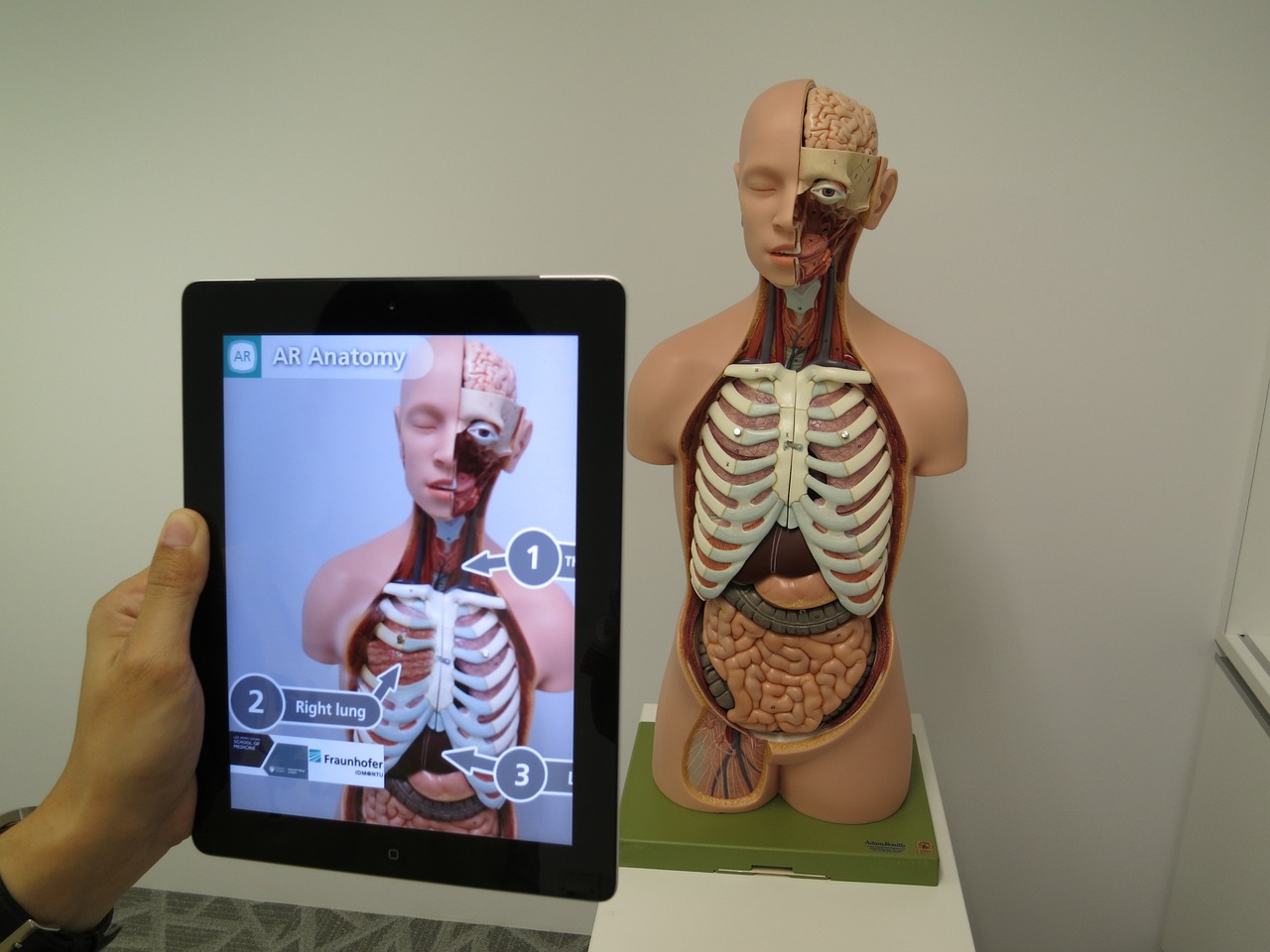
- Gaming and Entertainment: AR has revolutionized the gaming industry by creating immersive and interactive experiences. Popular games like Pokémon Go and Minecraft Earth use AR to overlay virtual content onto the real world, allowing players to interact with virtual objects in their real-life environment.
- Education and Training: AR is being used in education and training to enhance learning experiences. It allows students to visualize complex concepts, interact with virtual models, and engage in interactive simulations, making learning more engaging and effective.
- E-commerce and Retail: AR is transforming the way people shop in their everyday life by allowing them to try products virtually before making a purchase. Virtual try-on for cosmetics, furniture, and apparel is becoming increasingly popular, providing a personalized and interactive shopping experience.
- Healthcare and Medical Training: AR is being used in healthcare for surgical planning, patient education, and medical training. Surgeons can use AR to overlay virtual models onto the patient's body during surgery, aiding in precise and minimally invasive procedures.
- Architecture and Design: AR is revolutionizing the way architects and designers create and present their designs. It enables the visualization of 3D models in real-world environments, helping customers get a much better idea of the design and how they will fit into real-word environments.
Which devices can be used for augmented reality?
We will dive into the world of AR devices and explore the wide range of possibilities that exist to experience the exciting world of extended reality. From smartphones to smart glasses like RealWear and Google Glass or heads-up displays, we will uncover the mobile devices that can transport you into a whole new world of interactive and immersive experiences.
-
Smartphones and Tablets
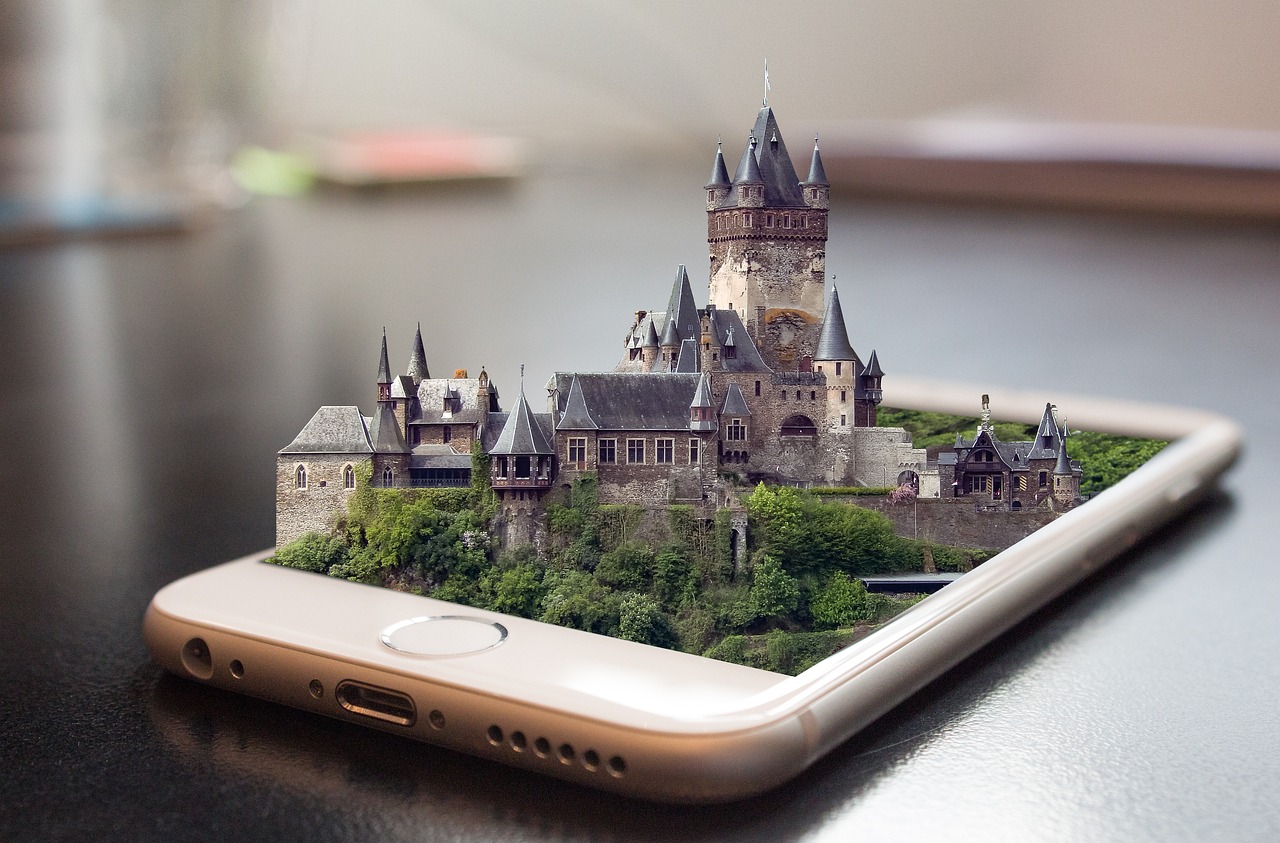

One of the most accessible and widely used devices for AR is smartphones and tablets. With their high-resolution displays, powerful processors, and advanced camera capabilities, smartphones and tablets are capable of delivering impressive AR experiences. By simply downloading AR-enabled apps, users can turn their handheld devices into a window to a virtual world that overlays digital content onto the real world. From games and educational apps to shopping and social media, smartphones and tablets provide a convenient and portable way to explore the possibilities of augmented reality.
Smart glasses are a type of wearable device that are specifically designed for AR experiences. These sleek and futuristic glasses are equipped with built-in displays, sensors, and processing power, allowing users to view additional content overlaid onto their field of vision. Smart glasses provide a hands-free and immersive AR experience, making them ideal for applications such as industrial training, remote assistance, and navigation. Some popular examples of smart glasses for AR include Microsoft HoloLens, Google Glass, and Magic Leap One.
-
Headsets and VR Devices
Although commonly associated with virtual reality (VR), headsets and VR devices can also be used for augmented reality experiences. These devices typically have more advanced sensors, cameras, and tracking capabilities, allowing for a more immersive and interactive AR experience. With headsets, users can be fully immersed in a virtual world where virtual content is overlaid onto their entire field of vision, creating a highly realistic and interactive AR experience. Examples of popular headsets that support AR include Oculus Rift, HTC Vive, and PlayStation VR.
-
Projection Devices
Projection devices are another interesting option for experiencing augmented reality. These devices use specialized projectors to project virtual content onto real-world objects or surfaces, creating an augmented view. Projection devices can be used for various applications such as interactive displays, art installations, and exhibitions. Some examples of projection-based AR devices include Projector-AR, Lightform, and Sony Xperia Touch.
-
Wearables and Accessories
In addition to smartphones, tablets, smart glasses, headsets, and projection devices, there are also various wearables and accessories that can be used for augmented reality experiences. For example, AR-enabled fitness trackers and smartwatches can overlay virtual content such as workout stats or navigation prompts onto the user's wrist. AR-enabled gloves or controllers can provide users with a more intuitive and immersive way to interact with virtual objects and real objects. These wearables and accessories can enhance the overall AR experience and provide new possibilities for interaction and engagement.
In conclusion, augmented reality can be experienced through a wide range of devices, from smartphones and tablets to smart glasses, headsets, projection devices, wearables, and accessories. Each device offers unique features and capabilities that can cater to different applications and use cases. Whether you are a gamer, a designer, a healthcare professional, or just someone who is curious about the world of AR, there is a device out there that can unlock the limitless potential of augmented reality and transform the way you perceive and interact with the world around you.
The benefits of augmented reality
As technology continues to evolve, augmented reality (AR) is making its way into various industries, including manufacturing. AR has the potential to revolutionize the manufacturing sector by offering numerous benefits that can enhance efficiency, productivity, and innovation. In this blog post, we will explore the specific benefits that can be achieved with AR in manufacturing, from improved design and prototyping to enhanced training and maintenance processes.
-
Enhanced Product Design and Prototyping
One of the significant benefits of AR in manufacturing is its ability to streamline product design and prototyping processes. With AR, designers can create virtual prototypes that can be visualized in the real world, allowing for better design validation and iteration before the physical product is manufactured. This can help reduce costly design iterations and shorten product development cycles, leading to faster time-to-market and improved product quality. AR can also enable design teams to collaborate in real-time, even when they are in different locations, allowing for more efficient and effective design reviews and approvals.
Augmented Reality (AR) can also enhance assembly and manufacturing processes in the manufacturing industry. By overlaying step-by-step instructions and real-time data onto physical objects, AR can provide real-time guidance to assembly line workers, reducing errors and increasing efficiency. Workers can visualize the correct assembly process, identify parts and components, and ensure that the assembly is done accurately and efficiently. This can result in reduced rework, improved productivity, and decreased downtime, leading to cost savings and increased operational efficiency.
AR and mixed reality can streamline maintenance and repair processes in manufacturing facilities. With AR-enabled devices, technicians can access digital information, such as maintenance manuals, troubleshooting guides, and repair instructions, in real-time, overlaying them onto the physical equipment they are working on. This can help technicians identify issues quickly, diagnose problems accurately, and perform repairs efficiently, reducing downtime and improving equipment uptime. AR can also provide remote assistance, allowing experts to guide technicians through complex repairs, even if they are not physically present at the site, leading to faster and more cost-effective maintenance and repair processes.
AR can significantly improve training and skills development in the manufacturing industry. With AR, workers can receive immersive and interactive training experiences that simulate real-world scenarios, allowing them to practice and improve their skills in a safe, controlled and simulated environment. AR can provide virtual training modules for equipment operation, safety procedures, and complex processes, allowing workers to gain hands-on experience without the need for physical equipment or risking safety hazards. This can lead to faster onboarding, reduced training costs, and improved workforce competency.
AR can also enhance safety and risk mitigation in the manufacturing sector. By overlaying digital information onto the physical environment, AR can provide real-time safety warnings, hazard alerts, and visual cues to workers, helping them identify potential risks and take appropriate actions to mitigate them. AR can also provide safety training and simulations, allowing workers to practice safety procedures and emergency protocols in a virtual environment. This can result in reduced accidents, improved safety compliance, and minimized risks to workers and the overall manufacturing process.
In conclusion, augmented reality (AR) offers a wide range of benefits in the manufacturing industry. From improved product design and prototyping to enhanced assembly and manufacturing processes, streamlined maintenance and repair, enhanced training and skills development, and increased safety and risk mitigation, AR has the potential to transform the manufacturing sector by boosting efficiency, productivity, and innovation. As AR technology continues to advance, manufacturers can leverage its capabilities to gain a competitive edge and stay at the forefront of the industry. Embracing AR in manufacturing can lead to improved processes, reduced costs, and increased competitiveness in today's fast-paced manufacturing landscape.
Contact us or make an appointment and get more insights, about the possibilities of Augmented Reality.
Augmented Reality FAQs
What is Augmented Reality (AR)?
Augmented Reality (AR) is a technology that overlays digital information such as images, videos, and 3D models onto a user's real-world environment. It enhances the physical world with digital elements, providing an interactive and immersive experience.
How does Augmented Reality work?
AR works by using a combination of devices such as cameras, sensors, and displays to project digital information onto the real world. These devices capture the user's physical environment and then overlay digital information on top of it.
Where is Augmented Reality used?
AR is used in many fields including:
- Education
- Medicine
- Entertainment
- Retail
- Industry
It can be used, for example, to enhance learning, perform complex medical procedures, improve the retail customer experience, and increase efficiency in manufacturing.
What are the benefits of Augmented Reality?
Augmented Reality offers many benefits. It can:
- Improve efficiency and accuracy in education and training
- Enhance the retail customer experience
- Present complex information in an easily understandable way
- Increase workplace safety by allowing users to practice dangerous situations in a simulated environment
What are the challenges in implementing Augmented Reality?
Implementing Augmented Reality can pose several challenges. These include:
- Technical challenges such as the need for powerful hardware and software
- Privacy and security concerns
- The need for accurate 3D modeling and tracking
- User acceptance and understanding of the technology
How does Augmented Reality differ from Virtual Reality?
While both technologies provide immersive experiences, there is a key difference: Augmented Reality adds digital elements to the real world, while Virtual Reality creates a completely digital environment. With AR, users can still perceive their physical environment, while VR transports them to a different world.