Condition monitoring is a crucial component of modern maintenance strategies. By continuously monitoring machines and systems, companies can minimize downtime and increase efficiency. One of the most advanced solutions on the market is ADTANCE PVM (Process Visualization and Monitoring), a platform that offers comprehensive real-time monitoring capabilities. In this article, the procedure for implementing a condition monitoring solution is described in detail using ADTANCE PVM as an example.
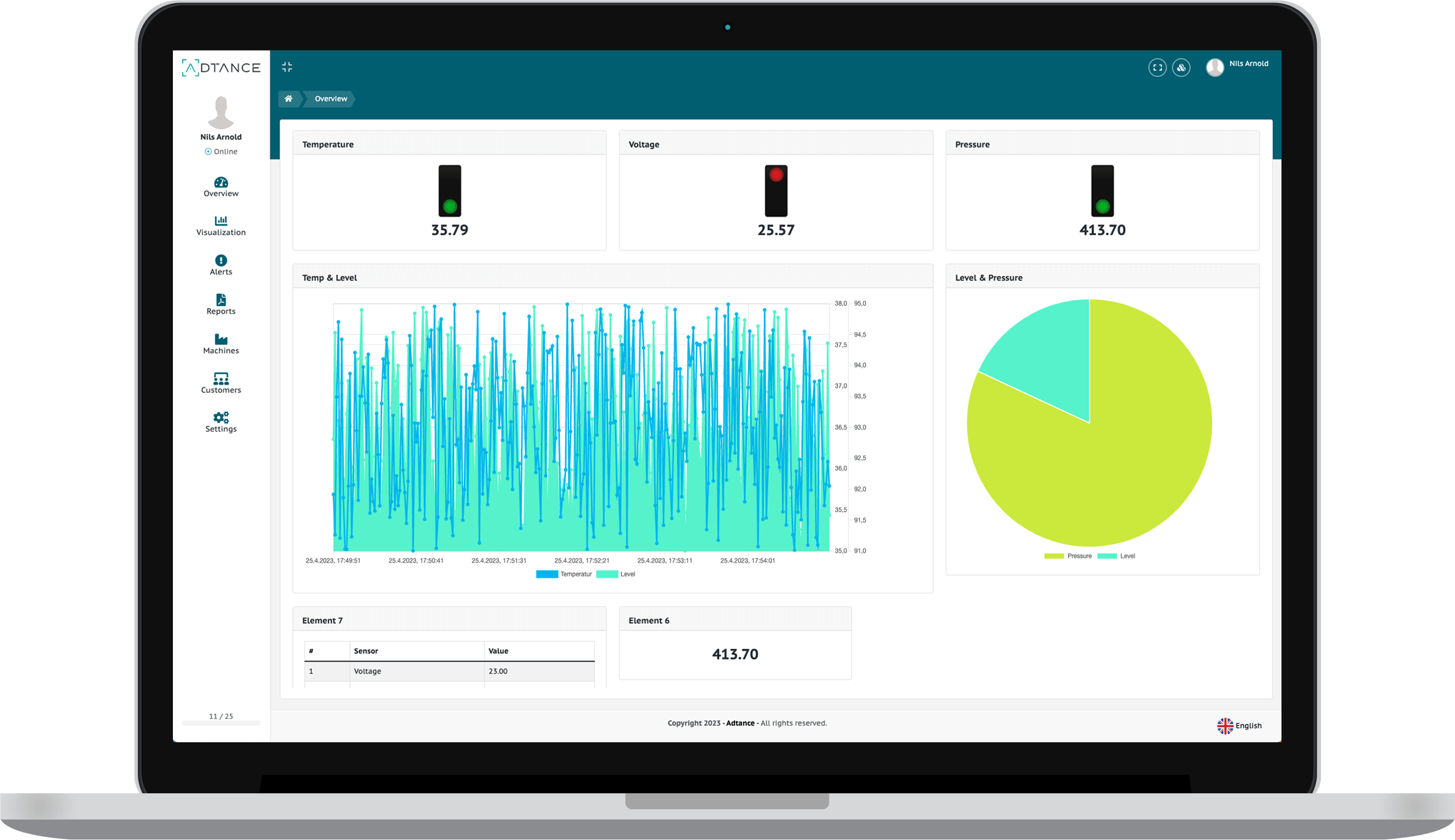
Overview of condition monitoring and ADTANCE PVM
Condition monitoring refers to the constant monitoring of the condition of machines and systems in order to detect potential problems at an early stage and take preventive maintenance measures. ADTANCE PVM is a specialized solution that integrates state-of-the-art technologies such as IoT (Internet of Things), Big Data and Artificial Intelligence to ensure precise and efficient monitoring.
Section 1: Preparation and analysis
1.1 Needs analysis and objectives
The implementation of a condition monitoring solution begins with a comprehensive needs analysis. Companies should clarify the following questions:
- Which machines and systems should be monitored?
- Which specific data and parameters are relevant?
- What are the main objectives of the monitoring (e.g. reduction of downtimes, optimization of maintenance costs)?
This analysis helps to clearly define the requirements and determine the objectives of the implementation.
1.2 Choosing the right technology and partner
ADTANCE PVM offers a wide range of functions and customization options. Companies should ensure that the chosen solution meets their specific requirements. The following factors play a role here:
- Compatibility with existing systems and machines
- Scalability of the solution
- Support and training options from the provider
-
Choosing the right partner to provide both the technology and the necessary support is critical to the success of the implementation.
Section 2: Technical implementation
2.1 Installing the hardware
The technical implementation begins with the installation of the necessary hardware components. This includes sensors that are attached to the machines and data transmission devices. The following steps must be observed:
- Selection and installation of suitable sensors
- Integration of the sensors into the existing machines
- Setting up the data transmission infrastructure
Correct installation of the hardware is crucial for accurate data collection and transmission.
2.2 Setting up the software
Hardware installation is followed by software configuration. ADTANCE PVM provides a user-friendly interface that allows for easy setup. Important steps are
- Software installation and configuration
- Integration of the sensors and devices into the software platform
- Setting up data transmission and storage
Careful software configuration ensures that all relevant data is collected and analyzed correctly.
Section 3: Data analysis and interpretationn
3.1 Data acquisition and storage
ADTANCE PVM enables the continuous acquisition and storage of machine data. The platform uses advanced algorithms to process large amounts of data in real time. Important aspects are
- Ensuring continuous and reliable data acquisition
- Establishing a secure and scalable database for data storage
- Use of cloud technologies for flexible data processing and storage
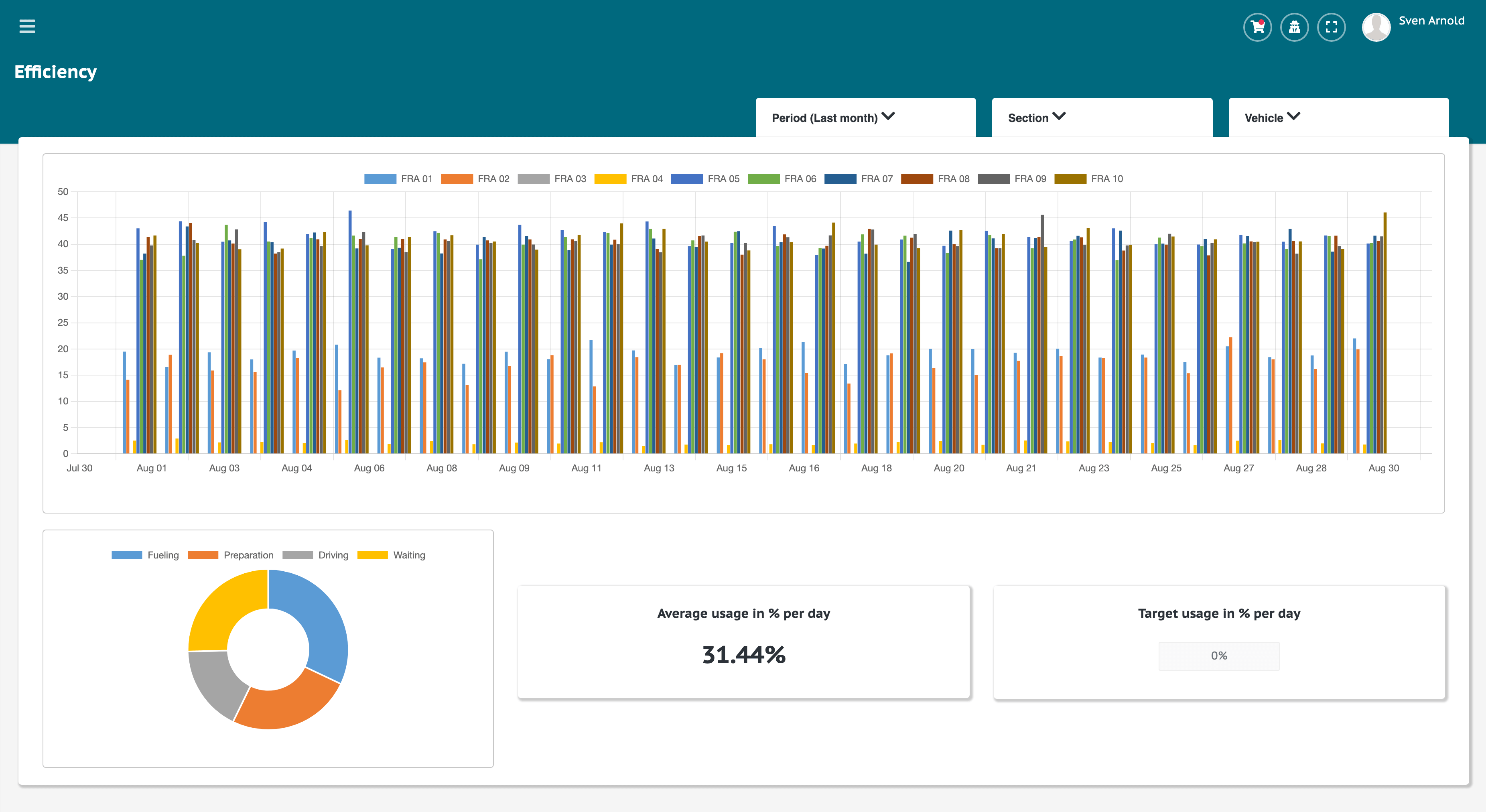
3.2 Data analysis and error detection
A key advantage of ADTANCE PVM is its ability to perform precise analysis through Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning. The steps include:
- Configuration of the analysis tools and algorithms
- Continuous monitoring and analysis of data
- Automated detection of anomalies and potential errors
The use of advanced analysis tools enables precise error detection and fast response times.
Section 4: Implementation and use
4.1 Implementation of maintenance measures
The collected and analyzed data serves as the basis for targeted maintenance measures. Companies should consider the following procedure:
- Developing and implementing a preventive maintenance plan
- Prioritization of maintenance measures based on the analysis results
- Training maintenance staff to use the platform efficiently
A well-structured maintenance plan helps to maximize machine availability and reduce costs.
4.2 Continuous improvement and optimization
After the initial implementation, it is important to continuously monitor and optimize the systems and processes. This includes:
- Regularly reviewing and adjusting the sensors and analysis tools
- Analysis of the collected data to identify optimization potentials
- Adaptation of maintenance strategies based on the analysis results
Continuous improvement ensures that the condition monitoring solution remains effective in the long term.
Section 5: Challenges and solutions
5.1 Technical challenges
The implementation of condition monitoring can be associated with various technical challenges, such as
- Integration into existing IT and OT systems
- Data security and data protection requirements
- Scalability of the solution
Solutions include working with experienced partners, using proven technologies and following best practices.
5.2 Organizational challenges
In addition to the technical aspects, there are also organizational challenges, such as
- Change management and employee acceptance
- Training and further qualification of staff
- Adaptation of existing processes and structures
Clear communication, comprehensive training programs and the involvement of employees in the implementation process are crucial for success.
Section 6: Success stories and best practices
6.1 Case studies of successful implementations
Analyzing case studies of successful implementations provides valuable insights and practical tips. Examples include:
- A manufacturing company that reduced downtime by 50% by implementing ADTANCE PVM
- A chemical company that reduced maintenance costs by 30% through condition monitoring
These case studies show the real benefits and the concrete approach to implementation.
6.2 Best practices for successful implementation
Based on the experiences from the case studies, the following best practices can be identified:
- A step-by-step implementation to minimize the initial investment
- Close cooperation with experienced partners and service providers
- Regular training and further education for staff
These best practices help to make implementation efficient and successful.
Section 7: Future prospects and developments
7.1 Technological trends
Condition monitoring technology is constantly evolving.Future developments include
- Use of even more precise and cost-effective sensors
- Further development of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms
- Integration of augmented reality (AR) to support maintenance
These technological trends will further improve the possibilities and efficiency of condition monitoring.

7.2 Market trends and business models
Market trends and business models are also changing. Companies should keep an eye on the following developments:
- Increase in as-a-service models in which condition monitoring is offered as a service
- Increased cooperation and partnerships between technology providers and users
- Increasing competition and decreasing costs for condition monitoring solutions
These trends offer companies new opportunities and possibilities to further optimize their maintenance strategies.
Conclusion
Implementing a condition monitoring solution such as ADTANCE PVM offers companies numerous benefits, from reducing downtime and optimizing maintenance costs to improving machine availability. Careful planning and step-by-step implementation are crucial to exploit the full potential of this technology. By continuously monitoring and adapting systems and processes, companies can benefit from the advantages of condition monitoring in the long term and strengthen their competitiveness.
With the steps and best practices described in this article, maintenance managers, service managers and business owners can ensure a successful implementation and sustainably improve the efficiency of their machines and systems.